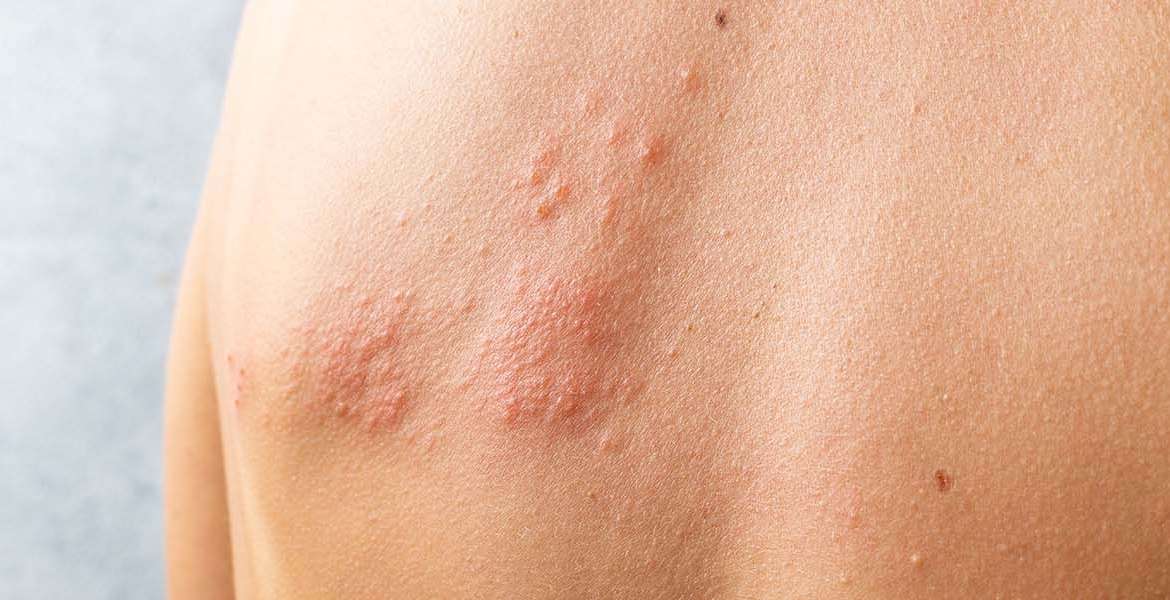
This disease, popularly known as "hives", causes extremely itchy rashes that are generally seen all over the body, slightly raised from the skin, with well-defined borders, of different sizes, red and sometimes pale in the middle.
It is acute or chronic
Urticaria and angioedema occur as clinical reflections of different mechanisms including the immune system and some inflammatory processes. Urticaria is classically divided into acute and chronic. Cases that last up to six weeks are called acute, and those that last more than 6 weeks are called chronic urticaria.
Skin symptoms of urticaria
They are red, edematous bumps that can be seen all over the body. Their sizes are very variable, they can be 1-2 mm or in the form of plaques covering large areas. They usually disappear within 24 hours without leaving a trace. It may manifest itself with swelling in areas where the skin is thin, such as the eyelids and genital area, or when it is deeply located, this is called angioedema. The bumps are usually itchy, and the itching increases at night.
What are the causes of urticaria?
The cause may not be found in 50% of cases. Medicines, foods, food additives, implants, contact and inhalant allergens may be responsible. The reaction develops within minutes. Acute urticaria due to medications is common and clinical findings usually appear within 36 hours after taking the medication. The most common drug group is antibiotics, especially penicillin, cephalosporin, tetracycline, and sulfonamides.
Bee stings, vaccines, blood products, shellfish, fish, milk, peanuts, potatoes, legumes, celery, parsley, carrots, spices, rice, bananas, apples and oranges are also considered triggers. Acute urticaria due to food is common and most of it goes unreported. In food allergies, the food itself may be responsible or added spices may contribute. Urticaria usually develops within minutes, but there are cases where urticarial lesions appear hours later as a result of slow absorption and metabolism of food. Rarely, there are foods that cause urticaria if exercise is exercised immediately after ingestion. Foods that cause urticaria with exercise are wheat, nuts and shellfish.
Urticaria may also develop for non-allergic reasons. Acetyl salicylic acid, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, radiocontrast agents, plasma expanders, local and systemic anesthetics should be investigated. Foods such as cheese, fish, meat, tomatoes, pineapple and avocado, which contain vasoactive amines such as histamine, or foods that release histamine, such as egg whites, cheese and strawberries, cause non-allergic urticaria.
Infections can also cause urticaria. It may develop following Epstein-Barr, Hepatitis B virus, and streptococcal upper respiratory tract infections.
chronic urticaria
Clinical conditions in which wheals persist for more than 6 weeks are called chronic urticaria. Physical urticaria accompanies 37% of the cases. Although the factor causing urticaria is rarely detected, triggering agents are investigated. Before autoimmunity was known to play a role, most cases were considered idiopathic. Stress is a trigger.
Types of chronic urticaria
- Dermographism (artificial urticaria): Formation of urticarial rashes as a result of trauma to the skin,
- Pressure urticaria: It is a deep swelling that is usually painful and occurs approximately 4-6 hours after pressure is applied to the skin. For example, painful swelling on the soles of the feet after walking for a long time,
- Cholinergic urticaria: Urticarial rash occurs after situations that increase body temperature, such as exercise, stress, hot shower,
- Cold urticaria: It occurs with contact with cold water or air,
- Solar urticaria: Urticaria that begins with sun contact,
- Contact urticaria: Urticarial rash that occurs minutes after some substances come into contact with the skin,
- Aquagenic urticaria: Urticaria that occurs after contact with water,
There are many types such as.
Causes of chronic urticaria
- Foods and food additives: Food-related allergic reactions were detected only in 3.5%. Nutritional additives are responsible for 10% (most commonly tartrazine, azo dyes, sodium benzoate).
- Inhalant allergens: Meadow grass pollens, mold spores, animal dander, house dust mites, cigarette smoke, chemical allergens,
- Systemic diseases: Lupus erythematosus, Sjögren's syndrome, IgM macroglobulinemia, more rarely thyroid diseases, lymphoma,
- Menstrual cycle and pregnancy: Urticaria may flare up during the premenstrual period. If it occurs only during menstruation, progesterone or estrogen sensitivity is suspected.
- Implants: Metals placed in the femur, metal dental prostheses, dental amalgam,
Psychological reasons: More common in cases of depression and anxiety.
Treatment
In the treatment of urticaria, if the cause is determined, it is important to stay away from it. Drug groups called antihistamines are often used in drug treatment. The dose can be increased under the control of your physician according to need. If necessary, more advanced treatments, vaccines and biological agents can be used in treatment.